Protecting Public Health through Effective Pest Control Measures
Introduction:
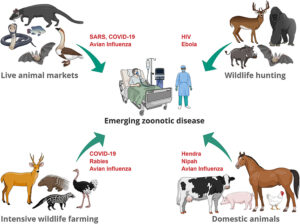
The world is currently facing a health crisis due to the spread of infectious diseases. While some of these diseases are caused by viruses and bacteria, others are transmitted through pests like rodents, mosquitoes, and ticks. These pests act as vectors, transferring diseases from one host to another, including humans. Therefore, pest control plays a crucial role in preventing the spread of infectious diseases, including zoonotic diseases.
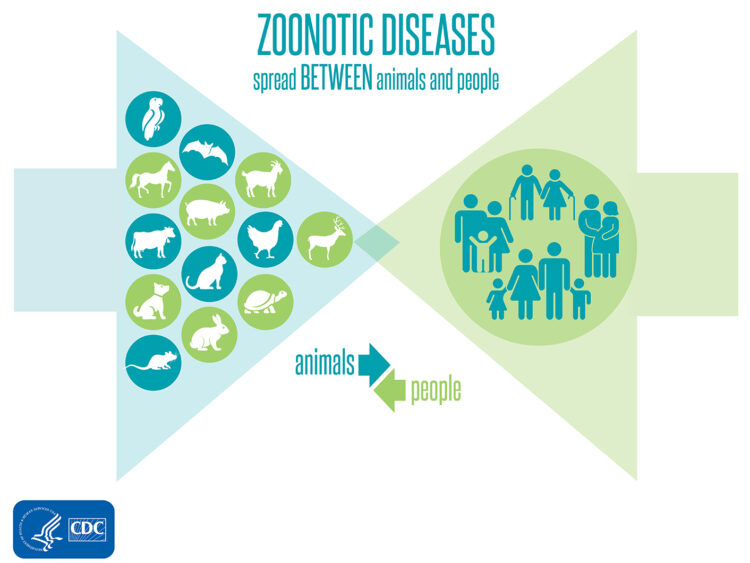
Understanding Zoonotic Diseases: Zoonotic diseases are infectious diseases that are caused by pathogens that can be transmitted from animals to humans. These diseases can be caused by a variety of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Some common zoonotic diseases include rabies, Lyme disease, and West Nile virus. Zoonotic diseases can spread through direct contact with infected animals or their bodily fluids, as well as through contact with contaminated surfaces or vectors such as mosquitoes or ticks.

What are Zoonotic Diseases?
Zoonotic diseases are illnesses that can be transmitted from animals to humans. These diseases can be caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites. Some of the most common zoonotic diseases include Lyme disease, West Nile virus, and rabies. Zoonotic diseases can be transmitted through direct contact with infected animals or their bodily fluids, through consumption of contaminated food or water, or through the bites of infected pests.
The Role of Pest Control in Preventing the Spread of Infectious Diseases:
Pest control measures are essential in preventing the spread of infectious diseases. Effective pest control helps to eradicate or reduce the population of pests that act as vectors for these diseases. This can be achieved through various means, such as the use of pesticides, trapping and removal, and habitat modification.
Pesticides:
Pesticides are chemical substances that are used to kill pests. They can be applied in various forms, such as sprays, baits, and fumigation. Pest control professionals use pesticides to target specific pests that are known to carry diseases, such as mosquitoes and ticks. However, it is essential to use pesticides responsibly and in accordance with regulations to avoid harming non-target organisms.

Trapping and Removal:
Trapping and removal are other effective methods of pest control. This involves using traps to capture and remove pests from an area. Pest control professionals use this method to target rodents, which are known to carry diseases such as hantavirus and leptospirosis. Trapping and removal are humane and environmentally friendly methods of pest control.
Habitat Modification:
Habitat modification is another effective method of pest control. This involves making changes to the environment to make it less conducive to the survival of pests. For example, removing standing water can help reduce the population of mosquitoes, which are known to carry diseases such as malaria and dengue fever. Habitat modification is a sustainable method of pest control that helps to prevent the spread of infectious diseases.
Pest control plays a crucial role in preventing the spread of infectious diseases, including zoonotic diseases. Effective pest control measures help to eradicate or reduce the population of pests that act as vectors for these diseases. Pest control professionals use various methods such as pesticides, trapping and removal, and habitat modification to achieve this. It is essential to use these methods responsibly and in accordance with regulations to protect public health and the environment.
Here are some additional details on the topic:
- Zoonotic diseases are a major global health concern. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), around 60% of all infectious diseases in humans are zoonotic in origin.
- Pest-borne diseases are a significant threat, especially in tropical and subtropical regions where pests thrive. For example, mosquitoes are responsible for transmitting diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus.
- Rodents are another significant vector for diseases, carrying pathogens such as hantavirus, leptospirosis, and plague. Rodents can also contaminate food and water sources, leading to the spread of diseases through consumption.

- Effective pest control measures require a multidisciplinary approach, involving public health professionals, pest control experts, and environmentalists. It is essential to consider the potential impact of pest control measures on non-target organisms and the environment.
- In addition to traditional methods of pest control, such as the use of pesticides and trapping, there is growing interest in alternative methods, such as biological control and genetic modification. These methods can be more sustainable and environmentally friendly than traditional methods.
- Public education and awareness are also critical in preventing the spread of infectious diseases. People should be informed about the risks of pest-borne diseases and how to prevent them through measures such as proper sanitation and hygiene practices.
- Finally, global cooperation is necessary to address the threat of pest-borne diseases. Diseases know no borders, and international collaboration is essential to prevent their spread. Organizations such as the WHO and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) play a vital role in coordinating global efforts to combat pest-borne diseases.
The Importance of Integrated Pest Management:
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is an approach to pest control that aims to minimize the use of chemicals and focuses on long-term prevention. IPM involves a combination of pest control methods, including biological control, habitat modification, and the use of non-chemical pesticides.
IPM is an effective approach to preventing the spread of infectious diseases because it takes a holistic approach to pest control. Rather than simply relying on chemicals to kill pests, IPM seeks to understand the ecology of pests and their interactions with the environment. By understanding the biology and behaviour of pests, IPM practitioners can implement measures that are effective in the long term.
For example, in the case of mosquitoes, IPM might involve reducing standing water and other mosquito breeding sites, promoting the use of mosquito nets and repellents, and using biological control agents such as mosquito fish or insect parasitic nematodes. By combining these measures, IPM can reduce the mosquito population and the risk of mosquito-borne diseases.

The Benefits of Effective Pest Control:
Effective pest control has numerous benefits, both for public health and the environment. Some of these benefits include:
- Reduced risk of infectious disease transmission: By reducing the population of pests that act as vectors for diseases, effective pest control can help prevent the spread of infectious diseases.
- Improved quality of life: Pests can be a nuisance, causing damage to property and reducing the quality of life for people. Effective pest control can help to prevent these problems and create a more comfortable living environment.
- Environmental protection: Effective pest control measures can help to protect the environment by reducing the use of chemicals and promoting sustainable pest control methods. This can help to preserve biodiversity and reduce the risk of pollution.
- Economic benefits: Effective pest control can have economic benefits by reducing the cost of healthcare associated with pest-borne diseases, reducing damage to property, and improving agricultural productivity.
Conclusion:
Effective pest control is essential in preventing the spread of infectious diseases, including zoonotic diseases. Pest control measures should be integrated, sustainable, and environmentally friendly. IPM is an approach that can help achieve these goals by combining different methods of pest control into a holistic approach. By working together, public health professionals, pest control experts, and environmentalists can help protect public health and the environment from the threat of pest-borne diseases.